22 Developer Experience
Learn how to check your Rust code for warnings and errors.
The use_extendr() function creates will create (or update) the settings.json file in Positron & VS Code. This lets the rust-analyzer find the Rust package. Rust files are automatically linted and checked for errors.
{
"rust-analyzer.linkedProjects": [
"${workspaceFolder}/src/rust/Cargo.toml"
],
"files.associations": {
"Makevars.in": "makefile",
"Makevars.win": "makefile",
"configure": "shellscript",
"configure.win": "shellscript",
"cleanup": "shellscript",
"cleanup.win": "shellscript"
}
}Viewing Problems
The rust-analyzer is always running and identifies errors and warnings as you write them.
You can diagnose and identify issues in your Rust code by using the problems tab.
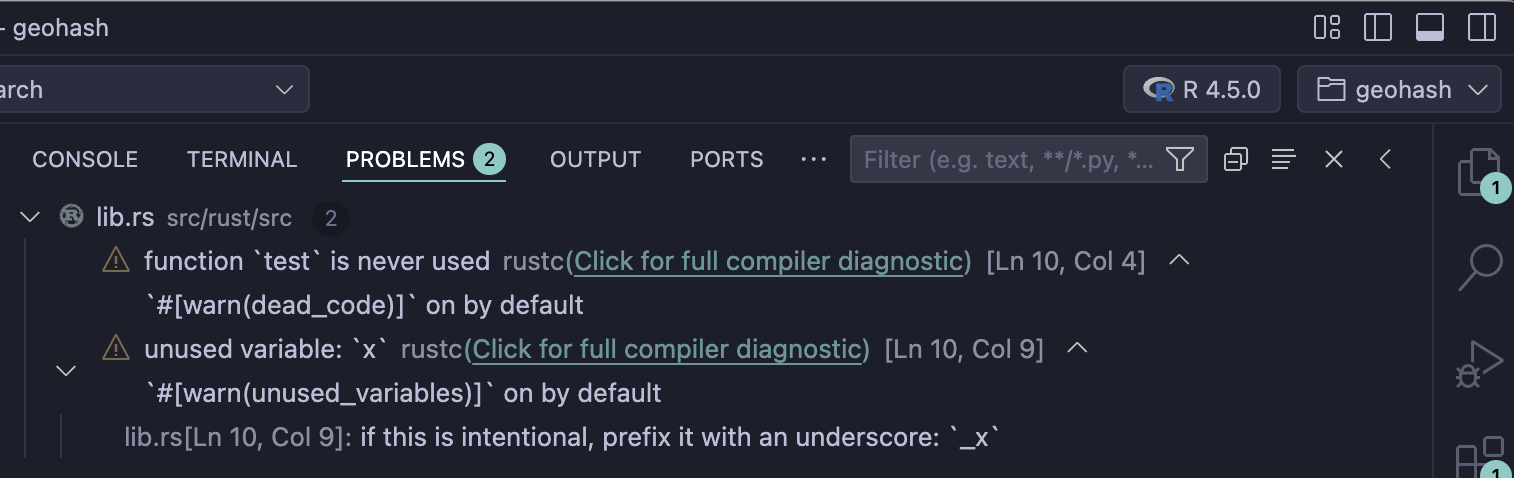
Or, alternatively, you can run cargo check from the terminal to get diagnostics that way. This is my preference, personally.
cd src/rust
cargo check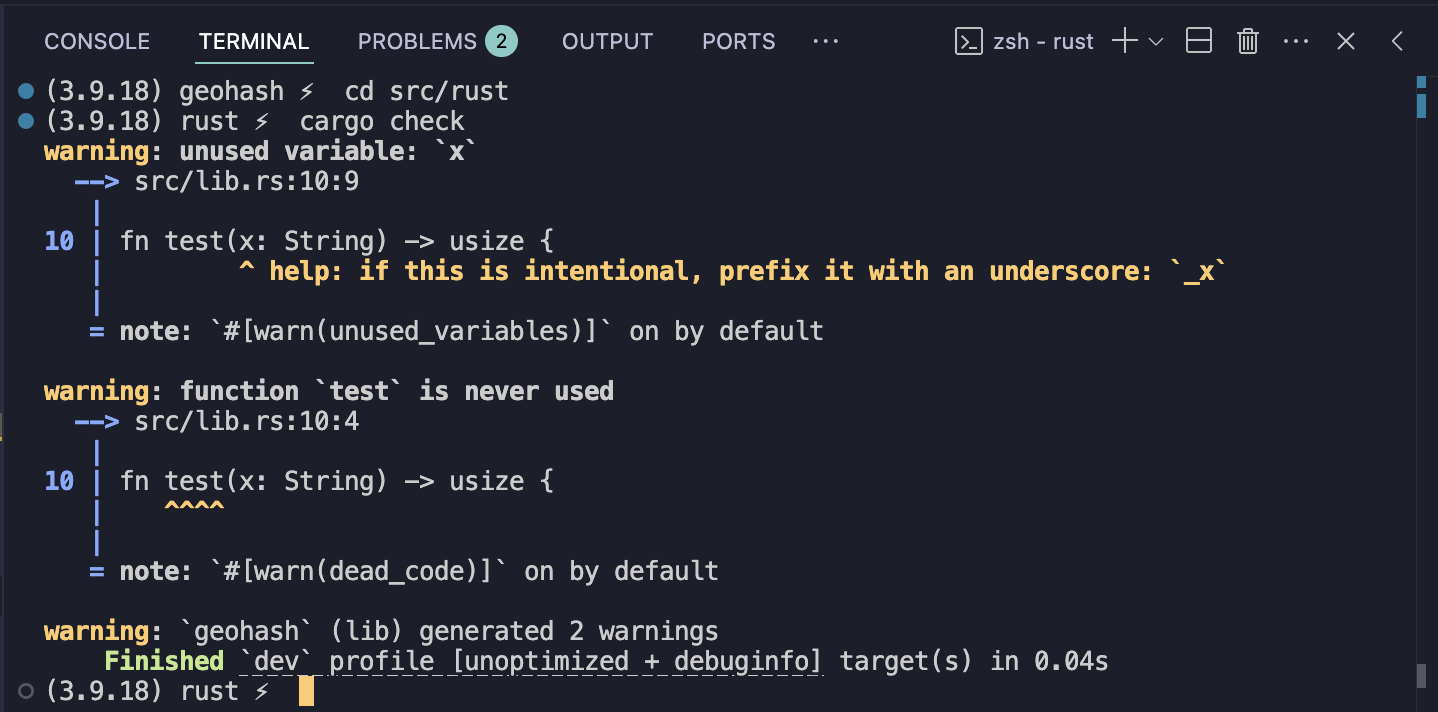
cargo checkcargo check Keyboard shortcut
I have a user task and keybinding to run cargo check in extendr packages that I find quite nice.
Open the command pallete using cmd + shift + p and find Tasks: Open User Tasks and add this task.
{
"label": "Check extendr package",
"type": "shell",
"command": "cargo check --all-features --manifest-path=src/rust/Cargo.toml",
}You can bind this task to a keyboard shortcut. I use shift + cmd + enter and the condition that the directory is an R package and the open editor is a rust file.
{
"key": "shift+cmd+enter",
"command": "workbench.action.tasks.runTask",
"args": "Check extendr package",
"when": "isRPackage && editorLangId == 'rust'",
}Exercise
- Run
cargo checkin thesrc/rustdirectory